The winter is coming. Need more clothes? No. Just get all kinds of Graphene heating product in PMA Group, such as Graphene heating waist and Graphene heating vest. Why we choose? Let us read the article from Nature PortfolioThermal insulation property of graphene/polymer coated textile based multi-layer fabric heating element with aramid fabric.

This study investigated the thermal insulation properties based on electrical heating test of graphene-based multi-layer fabric heating elements to confirm the possibility of application for fabric heating element for protective clothing. Four layers were designed as layers of outer, filler, electrical heating textile, and lining. The outer fabrics used two different densities of aramid woven fabrics (LD_ARW and HD_ARW), an aramid knit (AR_KT), and nonwoven (AR_NW). Fabricated graphene/polymer coated electrical heating textile (GR) exhibits a surface temperature of about 85 °C, a current of 0.12 A, and a power of 3 W when 30 V is applied. As composed with 4-layer, the surface temperature of LD_ARW and HD_ARW used as the outer for sample indicated less than 50 °C, due to their excellent heat resistance property; whereas, when AR_KT and AR_NW were used, the temperature was about 50 °C. This is because their fine fibers form high porosity that can entrap air. As a result of the thermal insulation properties, the temperature difference of each layer was in the order ΔT(GR-N3) < ΔT(GR-Lining) < ΔT(GR-Outer). In particular, when AR_NW was used as the outer fabric, ΔT(GR-Outer) was decreased by about 10 °C, compared with that of the other outer fabric. By the effect of relative humidity under dry 25% RH and comfortable 55% RH, the temperature difference was decreased under 55% RH; thus, the thermal insulation property was improved under comfortable humidity condition. Therefore, the best thermal insulation performance was exhibited when AR_NW was used as outer under 55% RH, and it is expected to expand its application to fabric heating element for protective clothing.
A cold environment results in a decrease in body temperature, and prolonged exposure causes cold-related illness, leading to numbness, frostbite, hypothermia, and eventually death. To maintain and protect the body temperature of the human body exposed to cold environments, clothing plays the role of a passive insulation layer, and is used to protect the human body from severe cold. In general, clothes have excellent thermal insulation from a stationary air layer that is formed between the fabric layers. In particular for winter clothing, thermal insulation properties play a crucial role for human heat maintenance. Thus, winter clothing consists of three or more layers of multilayer structure with different functions, in order to ensure thermal comfort in winter outdoor climatic conditions: (1)Outer layer: Protection against external environment, (2)middle thermo-insulating layer: thermal-insulation nonwoven or other thermal insulating material that protects the human body from excessive heat loss, (3) inner layer-lining: layer nearest to the human body that exchanges moisture and air between the human body and the environment. Passive and active methods are used to reduce heat loss through clothes. A passive method to increase thermal insulation is to increase the air layers of clothing using down filler or multi-layer clothes. In addition, when multilayer clothing is configured, the amount of air content varies, depending on the fabric type, structure, thickness, density, weight, and porosity of each layer, thereby affecting the thermal insulation property. In particular, in cold protective clothing for winter, a very important role is played by the middle layer, the basic function of which is to protect the human body against chilling. Different kinds of textile materials are used as the middle thermal insulating layer of multilayer clothing. An active method can be defined by providing extra heat using heating textiles or units, such as far-infrared, solar, chemically heated textiles, phase change material textiles or electrically-aided heating units.
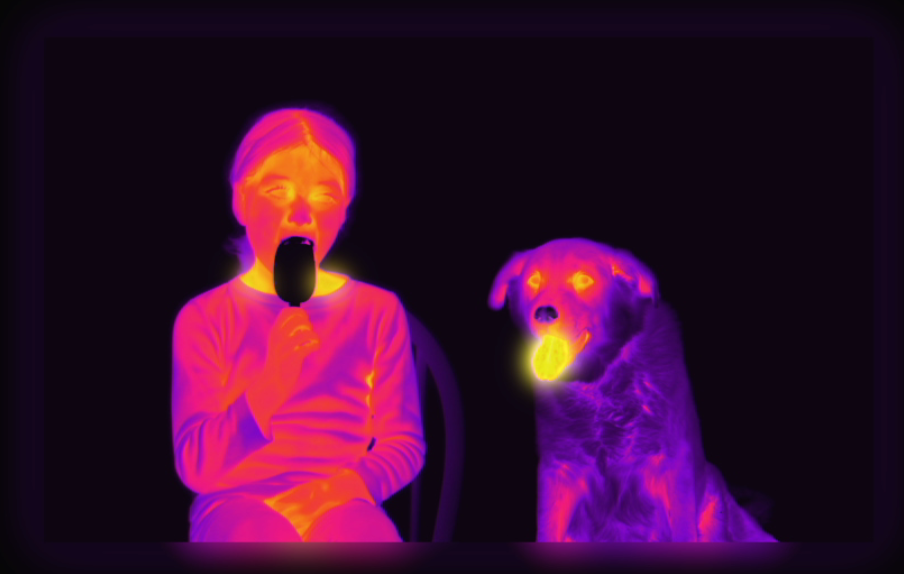
Electrical heating textile is one of the active methods for increasing thermal insulation value in cold protective clothing. It is mainly manufactured by conductive materials, such as copper, silver, or carbon-nano materials, on yarn or untreated fabrics. Generally, electrical heating garments mainly used by copper and stainless-steel materials. These materials are electrically stable due to the electrical resistance does not change during stretching, but those are easy to break as brittle properties. Accordingly, for providing stretchable to long metal wire, electrical heating textiles are manufactured by bending as a wound type, or coating nanoparticles on yarns. In the case of manufacturing a wound type with metal wire, there is a disadvantage that excessive heat is generated in the bending portion and can cause damage, and in the case of metal nanoparticles which form a conducive network are eliminated, thereby deteriorating performance. In recent, textile heating systems by coating with conductive inks or pastes such as carbon nano-based materials have a huge advantage due to their ability to bend and flex, and hence could provide heating effects for irregular geometries, such as tubular and spherical structures. In addition, since mass production is possible, they can be applied to various fields. Recently, the electrical heating textile is applied to heating garments, outdoor blankets, and sleeping bags, and research on electric heating performance, thermal insulation properties, and wearability has been continuously conducted. The people have reported the evaluation of the effects of heating protocols using graphene-heated clothing in cold environment. The graphene heater was located in the pocket of the upper back or chest of underwear. It was reported that graphene heater at upper back heating could increase the temperature and maintain the body temperature better, compared with chest heating. Another one have prepared a smart electrically heated sleeping bag to improve wearer’s thermal foot comfort in a cold ambient environment. The smart sleeping bag was aimed to maintain human feet within the thermoneutral range (25.0–34.0) °C. A smart electrically-heated sleeping bag consisted of nylon shell, nylon lining, filled with polyester fiber and flexible carbon polymer heating pad. Finally, it was developed to be able to provide wearers with an 8 h comfortable sleep in a cold environment. The rest have evaluated the heating performance of commercial heated vests of three types. The thermal images and the temperature between body and heating vests was investigated by IR camera. The results of evaluating the heating performance of three types of commercial heating vests differing in the type of material and the heating element constituting the heating garment were as follows. The film-type heating element showed the best performance when works itself. On the other hand, the human body wearing test results in the cold environment showed that the heat protection effect of the commercial heating vest with the filler and nonwoven-type heating element applied to the vest was the best. To design an excellent heating garment, it was reported that both the heating performance of the heating element and the thermal insulation properties of the heating garment itself should be considered.

Therefore, in this present study, in order to apply the horseshoe pattern electrical heating textile coated with graphene/polymer manufactured in previous study as protective garment, a graphene-based multi-layer fabric heating element was designed based on aramid-based fabric. After that, the surface temperature of each layer and the thermal insulation performance inside the layer of the designed samples were analyzed based on the electric heating test under 55% RH, which is the comfortable humidity condition. Moreover, in consideration of the environmental conditions used in extreme condition in winter, the thermal insulation performance based on electrical heating test was also measured under dry condition of 25% RH. The specific goals were as follows. First, the graphene-based multi-layer fabric heating element was finally intended to consist of four layers. The fabrics used in each layer were: (1)Outer fabric: two types of waterproof fabrics and two types of aramid woven fabrics, aramid knit and aramid nonwoven fabric. (2)Filler: neoprene textile horseshoe pattern electrical heating textile coated by graphene/polymer (below GR). (3) Lining: waterproof brushed PET fabric. After that, each sample was composed of 2-layer, 3-layer, and 4-layer textile based on GR as 1-layer; and then the temperature change and difference of each layer was examined by electrical heating test. Finally, to investigate the thermal insulation properties from the effect of relative humidity, four types of graphene-based multi-layer fabric heating element with aramid-based outer fabrics were investigated based on the electrical heating test at the conditions of (25 and 55) % RH.
